HOW TO PERFORM A TENSILE STRENGTH TEST ON PLASTICS ACCORDING TO ASTM D638
WHAT DOES IT MEASURE?
- Tensile strength – the amount of force that can be applied to a plastic before it yields (stretches irreparably) or breaks.
- Tensile modulus – how much a material can deform (stretch) in response to stress before it yields. Modulus is a measurement of the material’s stiffness.
- Elongation – the increase in gauge length after break divided by the original gauge length. Greater elongation indicates higher ductility.
- Poisson’s Ratio – a measurement of the relationship between how far a material is stretched and how thin it gets during the stretching process.
IS ASTM D638 THE RIGHT STANDARD FOR YOU?
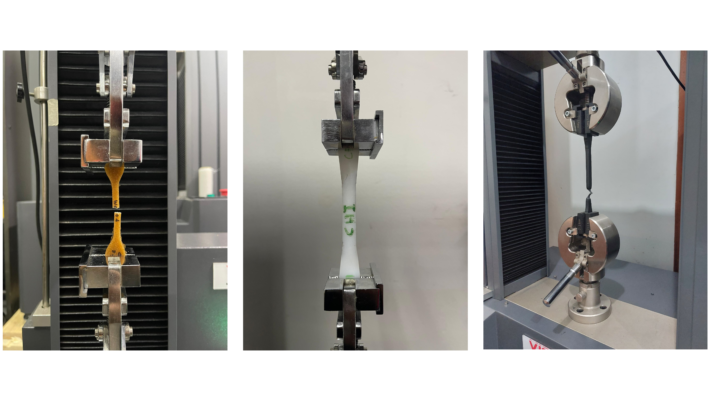
There are numerous test procedures for different types of plastics. ASTM D638 only applies to stiff plastic samples measuring 1.00 mm to 14 mm in thickness. If your sample is a sheet or film less than 1.00 mm thick, it should be tested according to ASTM D882. While ASTM D638 yields similar results to ISO 527-2, it is not deemed technically equivalent due to changes in specimen size and test parameters. While some large international firms test to both ASTM D638 and ISO 527-2, the majority of our customers prefer one standard over the other based on geography. North American manufacturers typically test to ASTM D638, where those in Europe and Asia largely test to ISO 527-2. Customers in Malaysia test to both ASTM D638 and ISO 527-2. The standard supports testing using different machine capacities, including systems such as the VEW 2308E, which offers high accuracy and stability for plastic tensile testing.All of these test methods are available in EvoTest Software, which are pre-configured method templates for the most common ASTM and ISO standards.
MATERIALS TESTING SYSTEM
GRIPS
SPECIMEN TYPES
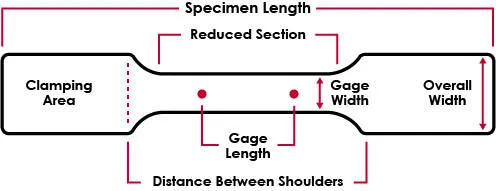
SPECIMEN MEASUREMENT
SPECIMEN ALIGNMENT
EXTENSOMETERS FOR ELOGATION TESTS
CALCULATIONS AND RESULTS
When presenting test results, it is critical to ensure that the words are correctly specified in order to comply with the standard and permit data comparison between laboratories. The most common mistake in data reporting is to report strain values using an incorrect source (extensometer instead of crosshead) which can lead to drastically different results.